Getting Started with ArgoCD Using Helm and Ingress
You’ve got a Kubernetes cluster up and humming. Now it’s time to deploy applications the GitOps way—with ArgoCD. In this guide, we’ll use Helm to install ArgoCD, configure an Ingress with cert-manager for automatic TLS, and wire up your Git repository (argocd-example) to manage application deployment.Why ArgoCD?
ArgoCD helps you manage Kubernetes the GitOps way. Everything lives in Git, changes are declarative, and you can see drift in real-time. It syncs your cluster with your repo and provides a dashboard, CLI, and API for managing everything.
Prerequisites
Before diving in, make sure you have:
- A working Kubernetes cluster (
kubectlconfigured) - Helm installed
- A domain name (e.g.
argocd.example.com) - A Git repo ready (we’ll use the argocd example app repo. https://github.com/argoproj/argocd-example-apps)
- An Ingress controller (e.g. NGINX or Traefik)
- cert-manager installed and a valid
ClusterIssuer - external-dns installed and configured
Step 1: Add the ArgoCD Helm Repo
helm repo add argo https://argoproj.github.io/argo-helm
helm repo update
Step 2: Install ArgoCD with Helm and Ingress Enabled
We'll install ArgoCD and configure it to use an Ingress and a TLS certificate automatically issued by cert-manager.
Let's create a values.yaml. Make sure you change the domain to be your domain.
global:
domain: argocd.example.com
configs:
params:
server.insecure: true
server:
ingress:
enabled: true
ingressClassName: nginx
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/force-ssl-redirect: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "HTTP"
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-dns
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostname: argocd.example.com
extraTls:
- hosts:
- argocd.example.com
secretName: argocd-tls
This tells ArgoCD to:
- Enable Ingress
- Use your domain (
argocd.example.com) - Request a TLS cert via cert-manager using
ClusterIssuer: letsencrypt-dns - Terminate TLS with a secret named
argocd-tls
Changeletsencrypt-dnsto your actualClusterIssuername if different.
- Adds a DNS record for
argocd.example.com
Apply the chart
helm upgrade --install argocd argo/argo-cd --namespace argocd \
--create-namespace --values=values.yamlStep 3: cert-manager Automatically Handles TLS
Since cert-manager is already running, it will see the cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer annotation on the ArgoCD Ingress and automatically:
- Issue a certificate using Let’s Encrypt (or your configured CA)
- Store it in the
argocd-tlssecret - Handle renewals automatically
You can verify that the certificate is issued and the secret exists:
kubectl describe certificate argocd-tls -n argocd
And confirm the Ingress is live:
kubectl get ingress -n argocd
Step 4: External-DNS automatically handles the DNS record
Visit https://argocd.example.com to see the ArgoCD login screen with a valid HTTPS cert.
Step 5: Log into ArgoCD
Get the default admin password:
kubectl get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -n argocd \
-o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d && echo
Install the CLI:
brew install argocd
or visit: https://argo-cd.readthedocs.io/en/stable/cli_installation/
Login using the CLI:
argocd login argocd.example.com --username admin --password <password>
Step 6: Connect Your Git Repository
Connect the argocd-example-apps repo to ArgoCD:
argocd repo add https://github.com/argoproj/argocd-example-apps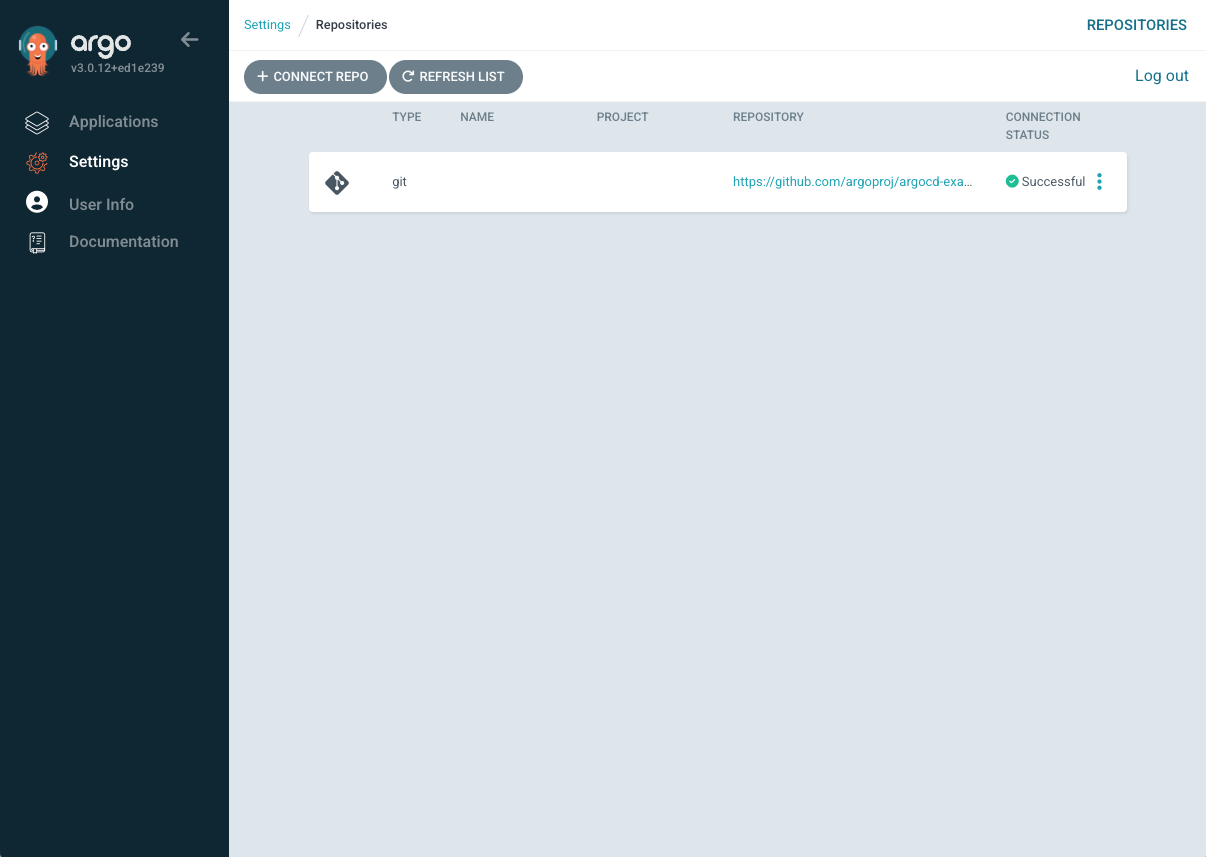
Step 8: Deploy Your First Application
Create an Application YAML in your repo:
# guestbook.yaml
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: guestbook
namespace: argocd
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/argoproj/argocd-example-apps
targetRevision: HEAD
path: guestbook
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: guestbook
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
Create the guestbook namespace to deploy the apps into
kubectl create namespace guestbookAnd deploy it with kubectl
kubectl apply -f guestbook.yamlOnce committed and pushed, ArgoCD will detect and sync the application automatically.
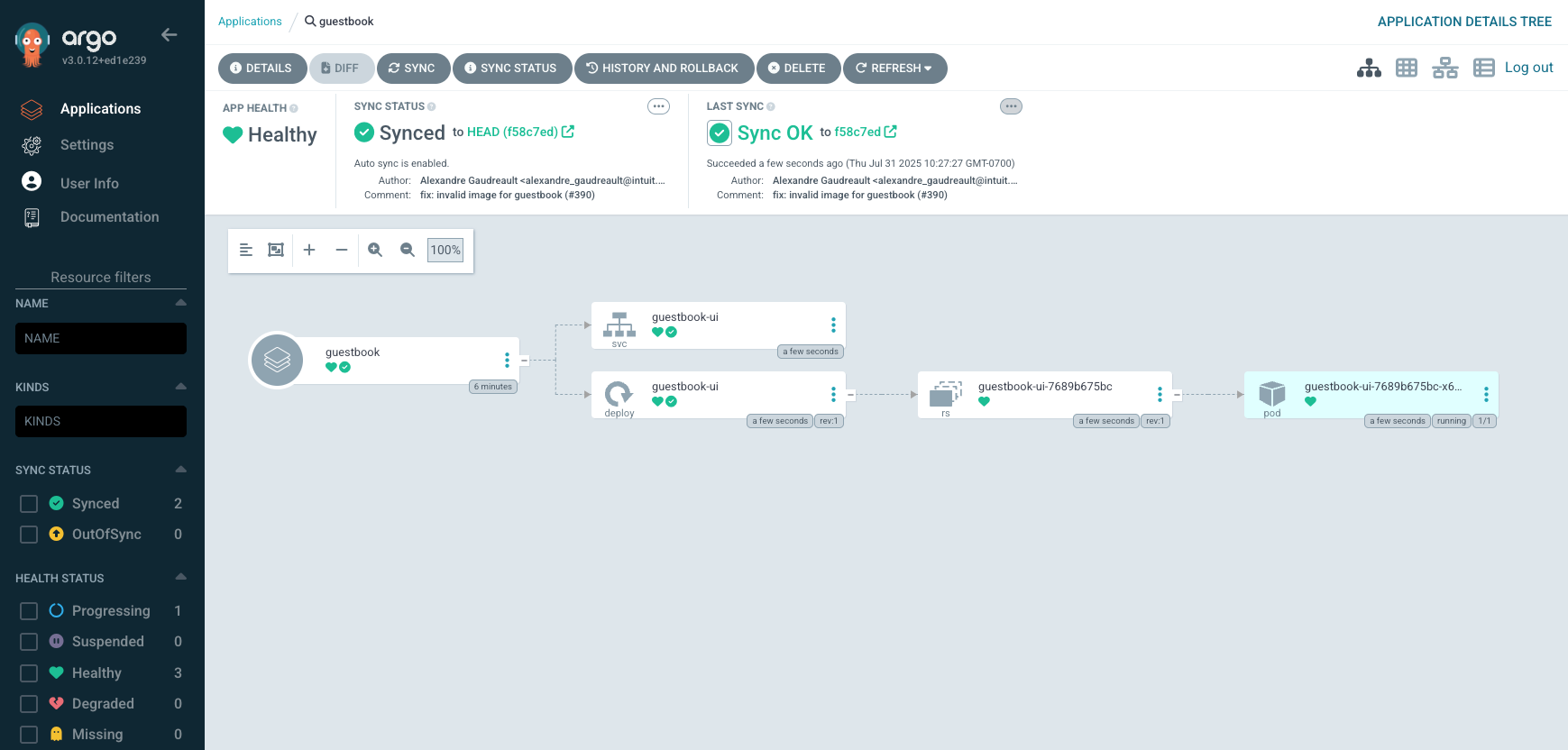
Wrapping Up
With ArgoCD installed via Helm and secured by cert-manager, you now have a GitOps pipeline ready to deploy and manage your Kubernetes applications.